
A patient has provided you with a prescription for their medication. The student is expected to check the prescription and contact the prescriber if any errors are found to rectify the mistakes. You do not need to counsel on the medication.
Please ensure that this scenario and mark scheme align with the most up-to-date UK NICE guidelines and the BNF when using it for your OSCE assessment.
You will need a student pharmacist, a patient, and a prescriber for this OSCE Scenario.
Novel/Direct Oral Anticoagulant Drugs (NOAC/DOACs)
You are a pharmacy student on placement at a community pharmacy. Your role is to counsel and support the patient who has come to pick up a prescription for Rivaroxaban. You need to check the prescription, action any errors if any are found and ensure proper communication with the prescriber.
Please discuss your prescription checking aloud. Do not worry about using jargon.
To do
You must perform a legal, accuracy and clinical check on this prescription using the latest up-to-date guidance.
If necessary, state any changes you wish to make to the prescriber. (second actor)
You have 10 minutes.
You have access to the BNF.
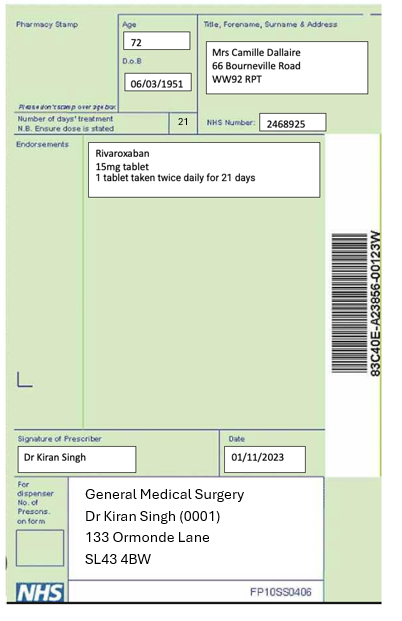
The Prescription:
Actor 1
You are Camille Dallaire (Cah-meel, Dah-lair).
Opening statement: “Hi, can I collect these tablets that I've been prescribed please?”
Patient Information:
Provide this information when prompted.
Medical History:
“Osteoarthritis.”
Medication History:
“Topical ibuprofen gel as required.”
Allergies:
“None.”
Indication for medication:
“I recently had a fall at home. This resulted in a broken hip.”
“I just had hip replacement surgery.”
“The doctor has prescribed these medications to stop a clot from forming in my legs.”
If the pharmacist mentions waiting for a new prescription:
“I was brought in by care staff, as I am in a wheelchair. I am frustrated, how long will this take?”
Actor 2
Prescriber Actor Information:
You are Doctor Singh.
Prescription Error:
The patient was prescribed rivaroxaban for VTE prophylaxis post hip replacement surgery. You should have prescribed 10mg once daily for 5 weeks, you have accidentally prescribed the treatment dose for a DVT. There is also an Interaction between Ibuprofen gel and Rivaroxaban.
The student should explain the query and a solution. When prompted:
“What would you like me to change and why”
“I apologise for this mistake – I will rectify it now.”
“I will send you a new prescription. Thank you.”





Any criteria marked in red must be met to pass this station.
 Red Flags missed: 5
Red Flags missed: 5
Referral Criteria for Anticoagulant Drugs
Refer to A&E if:
Severe Bleeding: Signs of severe bleeding, including uncontrolled bleeding from any site, or symptoms of major bleeding like significant blood loss, severe bruising, or black tarry stools.
Signs of Stroke: Sudden onset of symptoms such as numbness or weakness on one side of the body, difficulty speaking, or sudden loss of vision, which could indicate a stroke.
Severe Allergic Reaction: Severe allergic reaction symptoms like difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, or severe rash.
Acute Renal or Hepatic Failure: Symptoms of acute renal or hepatic failure such as confusion, severe fatigue, or jaundice.
Refer for Urgent GP Appointment if:
Persistent or Recurrent Bleeding: Ongoing or recurrent bleeding that does not resolve with basic measures, including frequent nosebleeds, bleeding gums, or minor wounds that bleed excessively.
Signs of Thrombosis: Symptoms of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or pulmonary embolism (PE) such as swelling, redness, pain in the legs, or sudden shortness of breath and chest pain.
Renal or Liver Impairment: Symptoms of worsening renal or liver function such as changes in urine output, swelling, or signs of liver dysfunction (e.g., abdominal pain, itching, dark urine).
NHS(2024)Anticoagulants. Available at:https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/anticoagulants/[Accessed 28 August 2024].
British National Formulary (BNF)(2024)Rivaroxaban. Available at:https://bnf.nice.org.uk/drugs/rivaroxaban[Accessed 28 August 2024].
This website uses cookies to ensure you get the best experience
Learn more